The workshop “Designing Accessible Extended Reality”, organised by the AutARK team at the Human and Computer Conference 2023, focused on how Assistive Technologies (AT) and Extended Reality (XR) can support people with various impairments (workshop at MuC). The aim was to raise awareness of the enormous potential of XR and AT, particularly in their ability to effectively support diverse user groups such as people with anxiety disorders, learning difficulties or autism spectrum disorder. It also aimed to motivate more research in this area in order to better understand and address the diverse needs of these target groups.
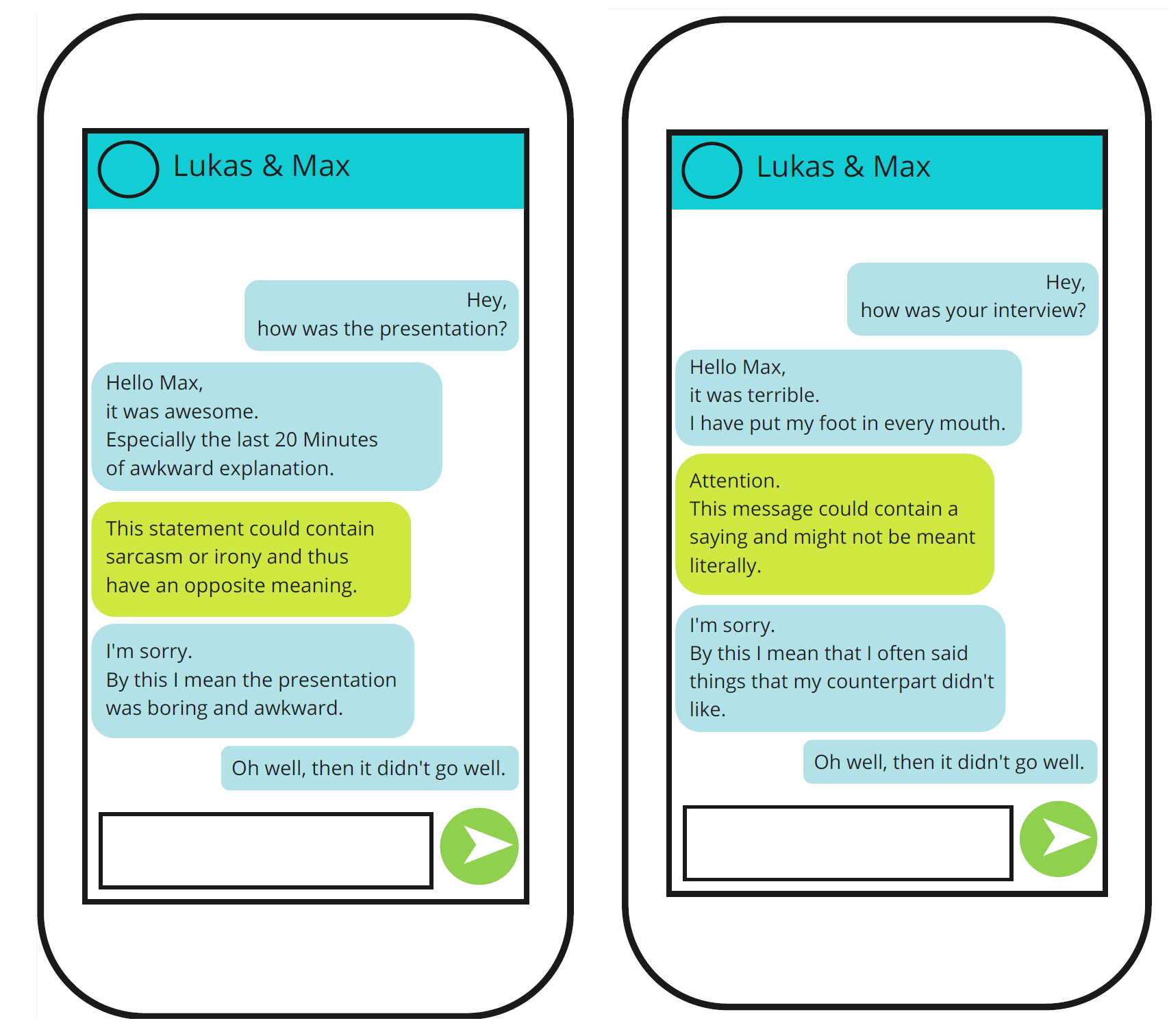
XR is defined as a spectrum of technologies ranging from purely virtual environments to extended real environments (cf. Zhang et al., 2023), such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR). There are several ways in which XR glasses can help in conversational situations, by supporting lip-reading or facial recognition. Another example of AT is the use of artificial intelligence to detect and highlight irony, proverbs or inappropriate comments in chats.

In the practical part of the workshop, 23 participants with broad expertise in usability, accessibility, XR, neurodiversity and autism spectrum disorders contributed to a diverse discussion. Challenges and solutions for three target groups in different contexts were developed and the requirements as well as social and ethical aspects that these target groups place on AT were discussed. Participants were divided into three groups: Autistic people in a leisure context, people with blindness or visual impairment in an educational context and people with hearing impairment in a professional context.
The first group identified communication support, reduction of sensory overload and consideration of the most inclusive solution as requirements for AT. Greater acceptance of the technology and greater awareness of the use of speech are necessary for its use. In general, challenges were identified in the areas of social interaction, sensory overload and time management, with solutions ranging from preventative measures to digital aids.
The second group sees the technological requirements in the consideration of privacy, time management and context sensitive assistance systems to support different types of visual impairment. Regarding the social and ethical aspects of AT, privacy issues, social considerations and self-determination play a central role. Access to learning materials, social interaction and mobility were identified as challenges in the educational context. Voice interaction, tactile interfaces and multimodal systems were discussed as possible solutions.
The third group sees the main requirements for the technology in the separation and detection of sounds and the reliability of the systems. Social and ethical concerns relate mainly to the constant monitoring of the environment, the risk of misinformation and possible stigmatisation by visible systems. In the professional context, two challenges were identified. The first is the failure to detect dangerous situations, e.g. in road traffic, and the second is communication in general. Smartwatches, XR glasses and hearing aids as input and output devices were proposed as solutions. In addition, the possibilities of using AI to detect hazards and the associated need to communicate the direction and distance of the source of the hazard were discussed.